Automatischer Drehmoment-Schlüssel 1/4" 10-50 Nm | Drehmomentschlüssel | Drehmoment-Werkzeuge | Handwerkzeuge | Stahl-Faust Onlineshop

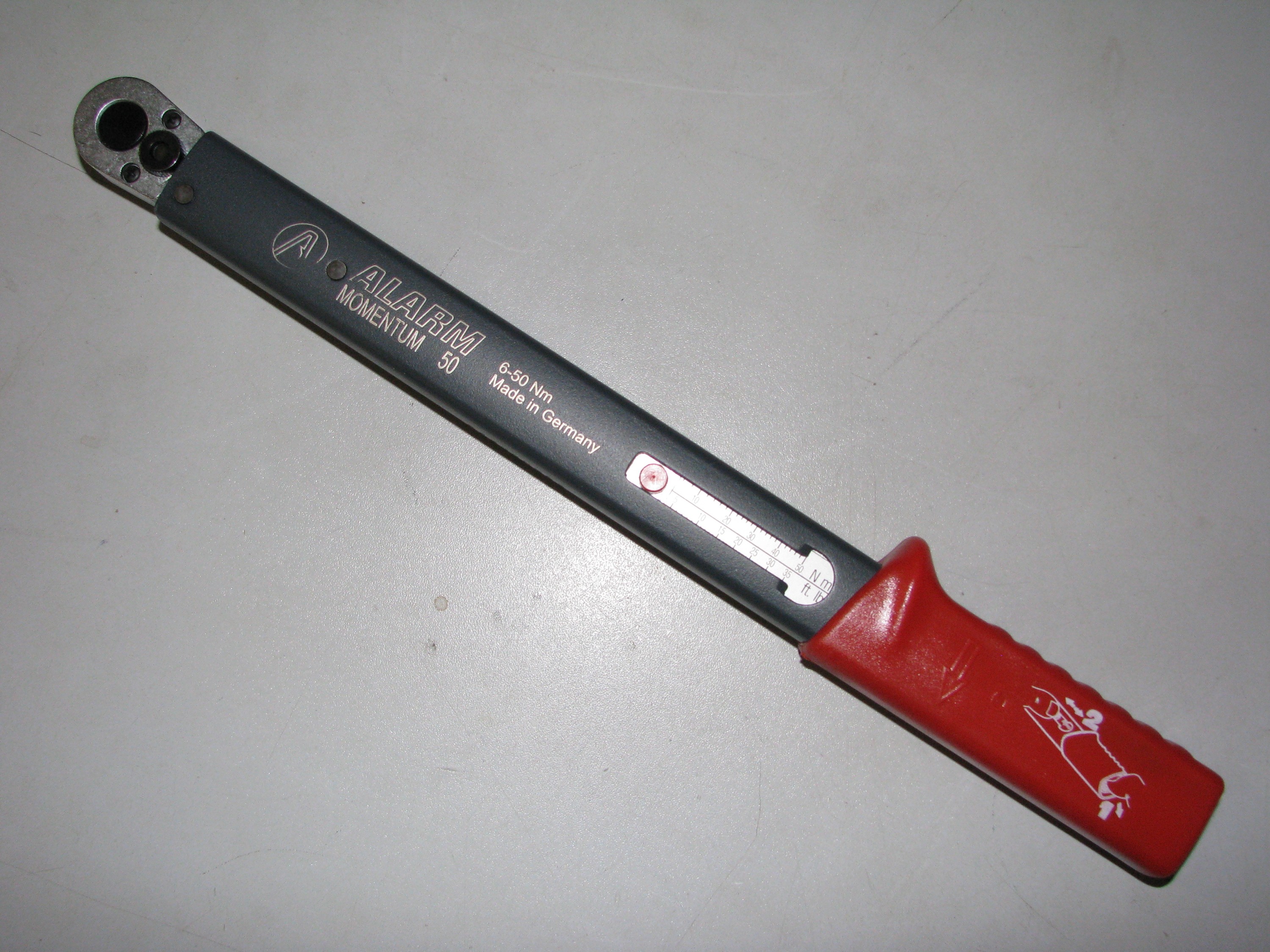
HAZET 6391-50 DREHMOMENT-SCHLÜSSEL 5 – 50 NM - Aufnahme 9 x 12 mm in Kr. München - Feldkirchen | eBay Kleinanzeigen ist jetzt Kleinanzeigen

Drehmoment Gedore Torcofix K 4549-05, 10-50 Nm, 3/8“ in Nordrhein-Westfalen - Voerde (Niederrhein) | Werkzeug Anzeigen | eBay Kleinanzeigen
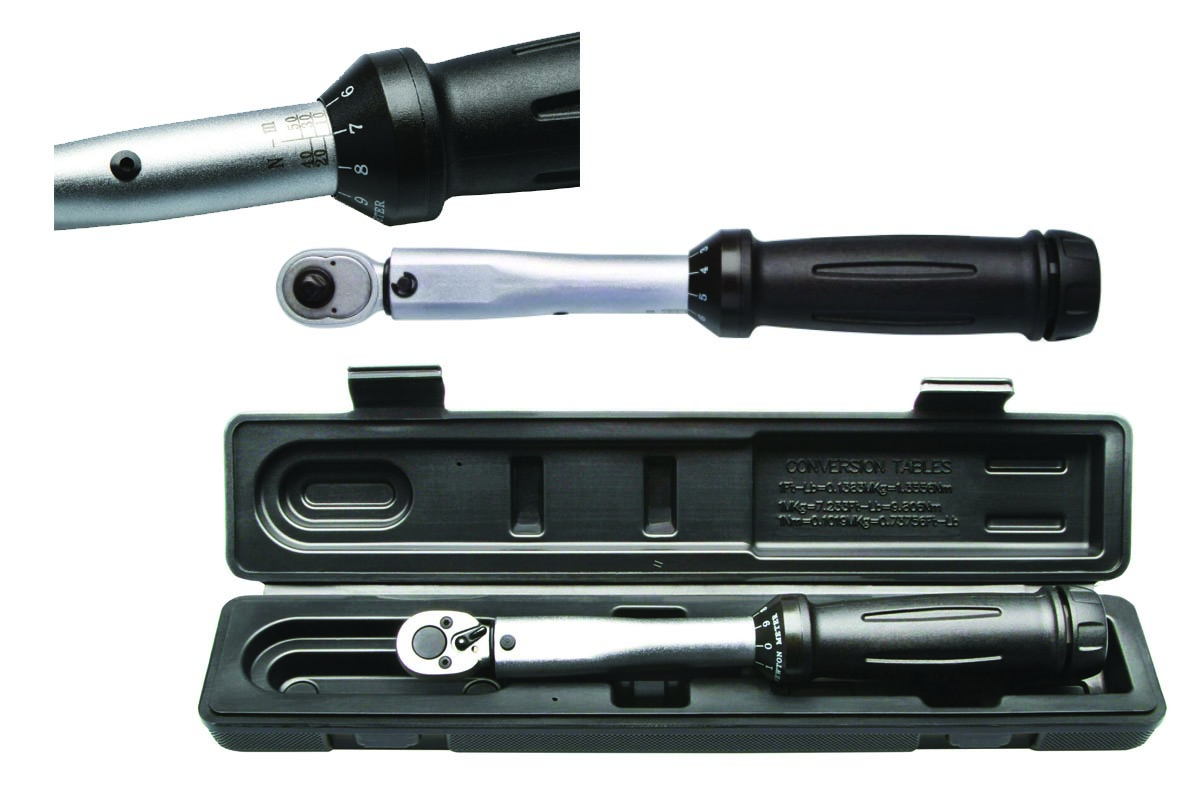

EVOTECH GERMANY KTM, BMW, TRIUMPH, DUCATI, APRILIA, HONDA, SUZUKI, KAWASAKI - Automatischer Drehmoment Schlüssel 1/4 Zoll 10 - 50 Nm Knarre Ratsche

Artikel 61205000 - Rutschnabe FS Drehmoment einstellbar 50-300 Nm vorgebohrt 19H8 Außendurchmesser 127mm max. Bohrung: 40mm Buchsenlänge 16mm

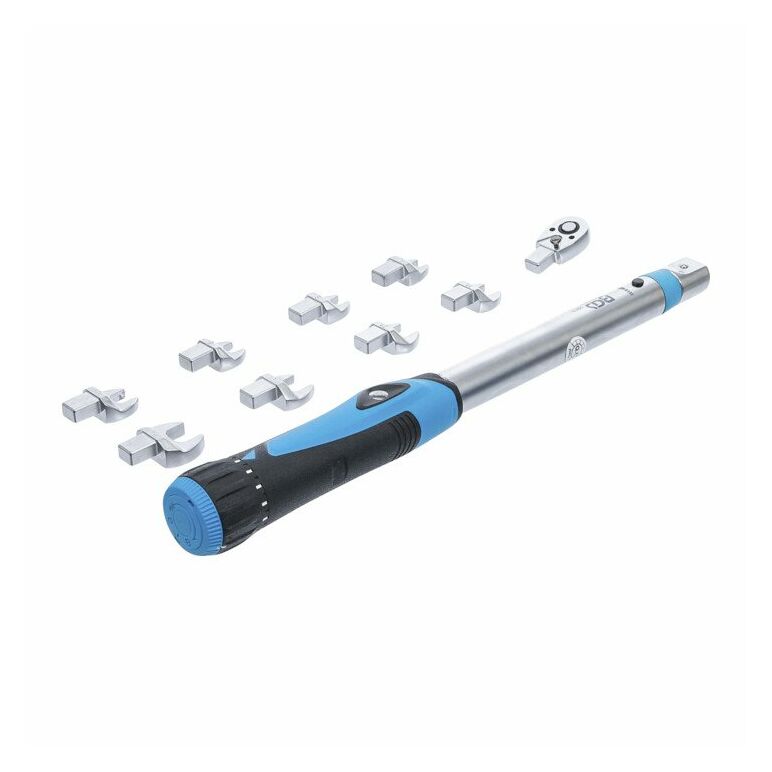
BGS 2813 | Drehmomentschlüssel-Satz | 6,3 mm (1/4") | 10 - 50 Nm | 10-tlg. | für 9 x 12 mm Einsteckwerkzeuge | Drehmoment-Schlüssel : Amazon.de: Baumarkt

Online Shop Jutger Remscheid. HAZET Drehmoment-Schlüssel 6391-50 ∙ Nm min-max: 5 – 50 Nm ∙ Toleranz: 2% ∙ Einsteck-Vierkant 9 x 12 mm
Mit einem maximalen Drehmoment von bis zu 50 Nm sorgt die Bosch Active Line Plus für eine harmonisch-agile Beschleunigung und ein „Plus“ an Fahrfreude auf Touren. - Bosch Media Service
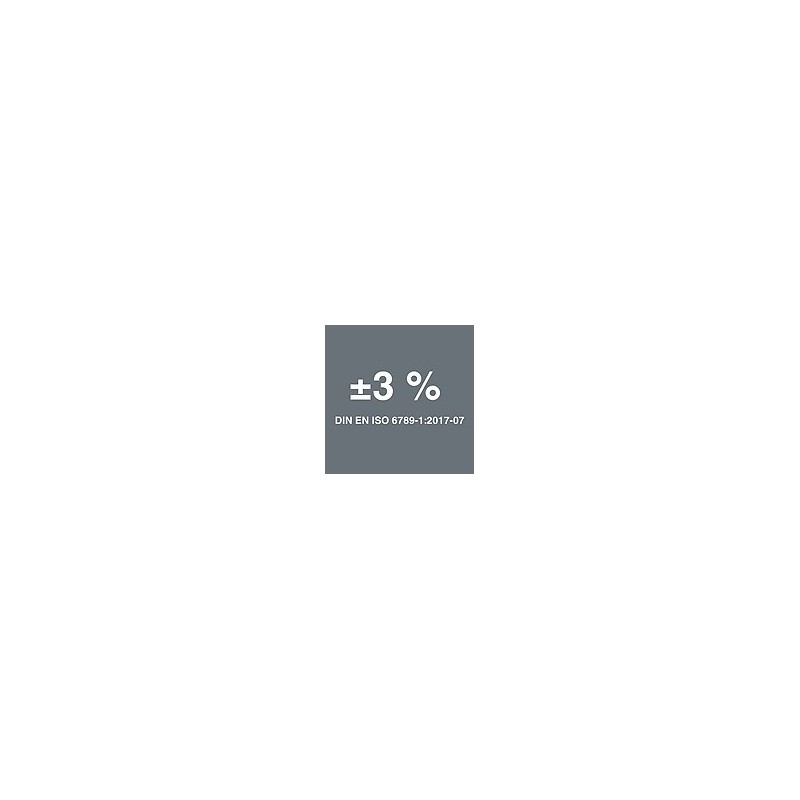
Wera Click-Torque B 1 Drehmomentschlüssel mit Umschaltknarre, 10-50 Nm, 3/8" x 10-50 Nm - 05075610001

















